An integral component of Perinatal medicine is a highly skilled neonatal assistance, based on the analysis of the current childbirth and pregnancy status of the fetus during gestational period, taking into account all risk factors, predicting the state of the newborn, and the provision of modern perinatal technologies of medical care to newborns.
After the birth is terminated the function of a placenta. A healthy newborn baby adapts to the conditions of extrauterine life. Physiological postnatal adaptation consists of the formation of breathing, blood circulation, thermoregulation, breastfeeding, physiological bacterial colonization of the newborn baby.
In Perinatal medicine are constantly faced with all sorts of infections, pneumonia, cardiovascular diseases, disorders of cerebral circulation.
Tasks of doctors the Perinatal Medicine:
- Regularly to observe for pregnancy of patients;
- On early terms to identify possible risks and to be prepared for them;
- Optimize the physiology of the pregnant woman to hold natural physiological childbirth;
- Psychologically prepare parents for the birth of a child;
- Organize family trainings;
- Nursing of children with small and extremely low birth weight.
Methods of Diagnosis
The method the ultrasound allows earlier in pregnancy to identify the majority of pathologies, including defects that are considered incompatible with life after birth.
Cordocentesis - invasive technique that allows not only to receive unbiased information on the presence and severity of disease, but also to treat the fetus in the womb. Similar operations are carried out strictly according to the testimony:
- For women over the age of thirty-five years;
- The presence of children in a family with a chromosomal abnormality or developmental disabilities;
- With hereditary diseases in close relatives;
- In cases of miscarriage earlier in pregnancy;
- If a deviation or defects detected by ultrasound.
Clinical Care
Possibility of complications from invasive procedures is small, but it can not be excluded. Any medical intervention in the body is considered to be potentially dangerous. May be mechanically damaged fetal bladder, the walls of the uterus, bleeding, infection of the fetus, miscarriage. So before you send a woman to such a diagnosis, the physician should evaluate how large the risk of complications.
Newborns with severe perinatal pathology, premature infants with a gestational age of 34 weeks or less, weighing two thousand grams or less, requiring prolonged intensive care, intensive nursing, further investigation, are translated into the intensive care unit, the pathology of newborns and premature infants children's hospitals.
Newborn Intensive Care delivers care to newborn infants through:
- Provision of critical care, including assisted ventilation, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, therapeutic hypothermia and many other modalities, by a multidisciplinary team of health care professionals;
- Transport of high-risk infants from referring hospitals. A neonatal team is available 24 hours a day, should a baby require immediate specialized emergency care;
- The evaluation and management of problems afflicting newborn infants, originating in the fetal or newborn period;
- Prenatal and postnatal counseling of parents and family members;
- Family-centered support that recognizes the emotional impact of having a sick newborn;
- Consultation with the full range of Pediatric medical and surgical specialists;
- Preparing infants and families for transition from the hospital to home.
Risk of violation of early postnatal adaptation is determined the following factors: hypothermia, hypoxia, hypercapnia, hypoglycaemia, perinatal infection, feeding with formula milk (without clinical evidence), etc.
Groups of risk Newborns
Newborns with perinatal pathology:
- Chronic, acute intrapartum hypoxia;
- Severe asphyxia;
- Birth trauma;
- Respiratory distress;
- Perinatal infections;
- Hemolytic disease of the newborn;
- Disorders of hemostasis;
- Anemia;
- Perinatal sepsis.
Newborns with impaired of intrauterine development:
- Immaturity (morpho-functional indicators of maturity of the child do not correspond to gestational age);
- A large weight before term of gestation;
- Prematurely born children;
Newborns undergoing long artificial lung ventilation:
- broncho-pulmonary dysplasia;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Antenatal observation of the pregnancy and fetal development include:
- Pregnant ultrasound for early detection of the formation of fetal malformations, control of fetal growth respectively to gestational age.
- Determining the status of placenta and causes of placental insufficiency.
- The use of Doppler ultrasound to determine the blood flow in the vessels of the placenta, umbilical cord, fetal brain.
- Determination of AFP in the blood of pregnant women at risk.
- Amniocentesis, placenta biopsy, the study of amniotic fluid in pregnant women at high risk.
- Screening for major pathogens of perinatal TORCH-infections, which are important in the formation of perinatal pathology.
- Cardiotocography (recording fetal heart rate during 30 minutes or more simultaneously with registration of fetal movement, uterine contraction).
This approach gives you the opportunity of objective timely fetal assessment, which is essential to improve the efficiency of perinatal care with observance Physiological bases of Obstetrics and Neonatology.
hide
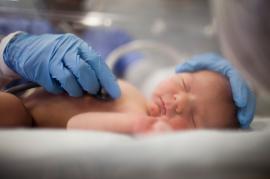 The Division of Perinatal-Neonatal Medicine is a nationally recognized group of neonatologists who provide care to premature and critically ill newborn infants, educate future pediatricians, neonatologists and neonatal nurse practitioners, and conduct research to understand mechanisms of disease, improve patient outcomes and advance medical education.
The Division of Perinatal-Neonatal Medicine is a nationally recognized group of neonatologists who provide care to premature and critically ill newborn infants, educate future pediatricians, neonatologists and neonatal nurse practitioners, and conduct research to understand mechanisms of disease, improve patient outcomes and advance medical education. 






