Interventional radiology is used especially in oncology, and extends its capabilities of conventional diagnostic techniques up to the active perform therapeutic procedures under the supervision of one of the types of radiation introscopy.
Interventional radiology - a subdiscipline of radiology, including methods of treating various diseases through the use of percutaneous, catheters, and other minimally invasive tools, without general anesthesia, controlled ray imaging techniques.
For procedures there is a limited number of contraindications, they are characterized by safety, low cost price, ease of implementation. All interventions can be divided into two categories - vascular and non-vascular interventions.
Of all interventional radiological procedures in cancer most often are performed the following:
- Biopsy;
- Drainage of pathological and physiological fluids (hematomas, abscesses, cysts, bile, urine);
- Prosthetics of tubular structures (vessels, bile ducts, trachea, ureters, digestive tube);
embolization or embolotherapy (ischemic and chemical effects on tumor tissue for the purpose of its destruction);
- Anastomosis (magnetic and puncture fistula for creating the conditions the passage of physiological and pathological substances);
- Extraction of foreign bodies (come off catheters in blood vessels);
- Installation cava filters for the prevention of emboli before and after major surgery in severe cancer patients;
- Hemostasis (transcatheter embolization of bleeding vessels and vascular fistulas after surgery);
- Thermoablation (destruction of the tumor tissue);
- Vertebroplasty (strengthening of the stricken from tumor vertebral body).
Vascular Radiology:
- Arterial angioplasty at the peripheral and central vascular pathology.
- Fighting against pathological thrombus formation.
hide
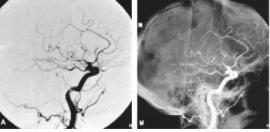 Interventional radiology - area of medicine, which includes a complex of the sequential execution of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures under fluoroscopy, ultrasound, computed and magnetic resonance imaging.
Interventional radiology - area of medicine, which includes a complex of the sequential execution of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures under fluoroscopy, ultrasound, computed and magnetic resonance imaging. 






