Cytopathology in gynecology
Timely diagnosis of various gynecological diseases - an important component of their successful treatment. Cytological analysis of cervical cells helps on time find widespread oncological disease - cancer of the cervix.
What is cytologic analysis?
In carrying out cytological analysis is examined tissue cells, their number, shape, mutual position, and other characteristics. The most important is ability to detect precancerous changes in cervical cells.
Since these changes do not manifest themselves in the overall health of women, by the other ways their find difficult. Material for the study take by scraping a very small amount of tissue from the surface of the cervix with a spatula, spoon, or a probe.
The study itself takes place under the microscope. In many clinics conducted simultaneously the study of cells in different ways. An integrated approach allows you to get more accurate results. Assessment of the condition individual cells and overall assessment of the material gives you the opportunity diagnose the disease, or to talk about that a woman is healthy. According to results of analysis is made cytologic conclusion.
The results of cytological analysis
The analysis results are evaluated by the five states of the cellular tissue (stage of the disease or classes):
- Cells with anomalies are absent - a woman is healthy.
- Cells have minor changes denominated in a slight increase of the nucleus. The analysis is considered normal in terms of having cancer, but most often this stage suggests inflammation or infection. A woman is recommended to pass an additional examination in order to establish the causes of the presence of abnormal cells of the second stage.
- There are cells with significant pathological changes of the nuclei. The number of such of cells is low, but if the detected cells in this step is required additional analyzes.
- Cells have significant heavy atypical changes that can be considered a precancerous condition.
Detection of typical cancer cells
Cervical cytology in this interpretation allows you to define the following conditions:
- No pathological changes
- Various atypical state of cells including cervical dysplasia (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia)
- Сarcinoma (cancer) of the cervix.
Difference cancer from normal epithelial of cells is based on differences in size, shape and color, as well as improper distribution of nuclear chromatin (as irregular clusters).
Besides the cancer cells the cytologic specimen have a large number of leukocytes, particularly polynuclears, bacteria, elements of red blood.
hide
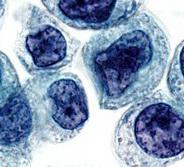 Cytopathology - section pathology, that studies during pathological processes at the level of the cell and its components. Cytopathology explores causes of tumoral formation.
Cytopathology - section pathology, that studies during pathological processes at the level of the cell and its components. Cytopathology explores causes of tumoral formation. 






