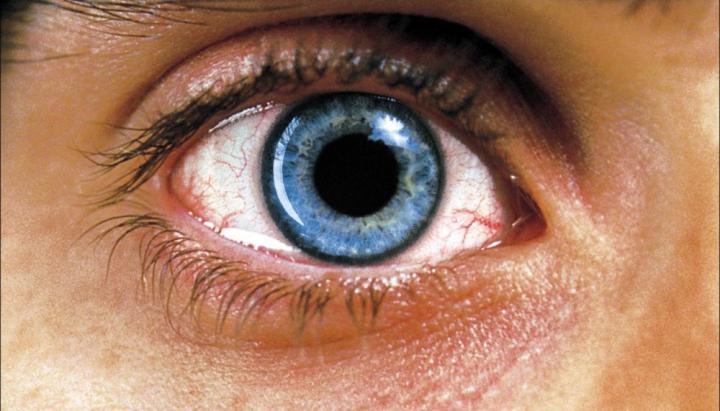
General characteristics of the disease
When colds, metabolic disorders, immune and autoimmune processes, the choroid is involved in inflammation, which occurs predominantly in the anterior part of choroid (iritis or iridocyclitis) - anterior uveitis or posterior parts of it - posterior uveitis (with the defeat of the choroid).
Distinction is also made generalized uveitis when there are vitreous opacities, exudative lesions in the choroid and secondary changes in the cornea and lens.
Uveitis, classified by course and by a nature of the inflammation. At the first sign they are divided into acute and chronic, by nature of an inflammation - the serous, exudative, fibrinous-plastic, purulent and hemorrhagic. The clinical picture depending on the etiology can be very diverse. Often, the disease takes a protracted, when the periods of exacerbation in one or both eyes alternately or simultaneously replaced by remissions.
Causes of uveitis Eye
Often, the cause the development of uveitis are infectious diseases: brucellosis, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, tuberculosis, as well as such common diseases as rheumatism and diabetes. In addition, eye injuries are frequently accompanied by uveitis.
Without timely treatment of uveitis may lead to an increment of the lens to the pupil, cataracts, secondary glaucoma, edema or retinal detachment, clouding of vitreous eye.
Symptoms of uveitis Eye
Symptoms of uveitis differ depending on the type of disease. Typical symptoms of anterior uveitis:
Among the characteristic symptoms of uveitis peripheral type:
Symptoms of uveitis posterior occur quite late. For this species of inflammation of the choroid are not typical pain or redness. The most common at a posterior uveitis manifests itself a gradual decline of view, distortion of objects and blurring of vision.
Treatment of Uveitis
The complexity of effective treatment of uveitis due to the fact that even with the most careful examination, reveal the true cause of their not always possible. Therefore allopathic pharmacotherapy of uveitis has an overall pathogenetic directivity and includes general and local anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, vasodilators, immunostimulatory therapy, enzyme therapy, physiotherapy and hirudotherapy.
Scheme treatment of uveitis depends on the etiology and type of disease. However, any form of inflammation symptomatic treatment of uveitis involves the prevention of destruction of the structure of vitreous eye and lens.
The medical treatment of uveitis streptococcal etiology are used broad-spectrum antibiotics, corticosteroids and vitamin therapy. Extinction of the inflammatory process occurs approximately at 3-5 day of treatment.
Uveitis with tuberculosis etiology stoped by with the help by TB chemotherapy. In severe cases with significant destruction vitreous eye sometimes is required carrying out surgical treatment of uveitis.
In recent times attempts are made supplement the approved methods of allopathic treatment of this pathology with homeopathic medicines. Since for its implementation the doctor should not only be a homeopath, but also an experienced ophthalmologist, only a clear understanding of the pathogenetic mechanisms of the development of uveitis allows to succeed in applying the method of homeopathic therapy.
Leave a Comment